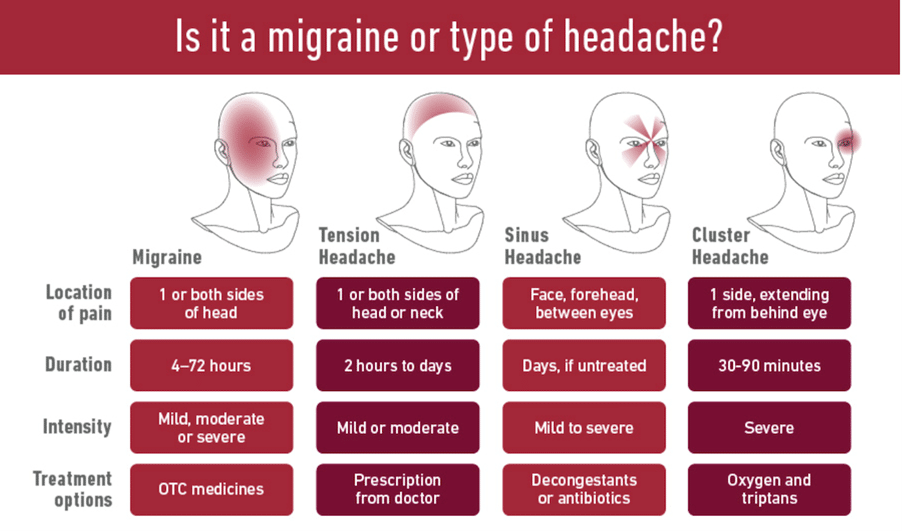
When there is pressure or pain in your head, it can be difficult to tell whether you are experiencing a typical Headache or a Migraine. Let explore and see if we can differentiate between the two.
What is a Headache
Headaches are no fun and the most common type of pain that most people experience. Some can range from a feeling of slight pressure behind the eyes to really severe pain that can last for weeks. Most headaches are not medically serious, but some can be symptoms of more dangerous problems, so they should not be ignored.
There are many different types of headaches, which have been broken down into two main groups; primary and secondary.
What is a Primary Headache?
A primary headaches when the headache itself is the main problem and has no known underlying cause. Pain usually linked with primary headache comes from the inflammation of pain sensitive structures in your body. Examples of primary headaches include:
- Migraine Headache
- Tension Headache
- Cluster Headache
There are certain causes that can affect a primary headache
- Stress
- Alcohol
- Changes in your sleep pattern
- Specific Food
- Missing meals leading to low blood sugar
What is a Secondary Headache?
A secondary headache usually occurs from another medical condition that triggers pain sensitive areas in the neck and head. They typically start from nowhere and the pain can become unbearable. Although secondary headaches are uncommon, it could be a warning sign to something more serious so it should not be ignored. Some of these include:
- Brain tumour
- Neck or brain injury
- Stroke
- Severe hypertension
- Bacterial or viral meningitis
There are certain symptoms to look out for with a secondary headache
- Headaches after fainting or a seizure
- A new or different type of headache in someone over 50 years old.
- Headaches that wake you up from your sleep.
- Increased frequency or severity of a headache
If you are experiencing a headache of unknown cause or seem to be having frequent headache without warning. Contact your healthcare provider for further advice and guidance. They may recommend a physical examination.
What is a Migraine
Migraine is a common health condition, affecting around 1 in every 5-15 adults. Some people have migraines frequently, up to several times a week. Other people only have a migraine occasionally. It’s possible for years to pass between migraine attacks. Migraines can be extremely debilitating causing severe throbbing headaches on one side of the head. In some cases, the pain is often described as a severe, dull, steady ache. It may start as a mild pain but soon becomes unbearable without migraine treatment.
Symptoms of a Migraine
There are many symptoms’ people experience with a migraine attack such as:
- Pain usually on one side of your head, but often on both sides
- Pain that throbs or pulses
- Sensitivity to light, sound, smell and touch
- Nausea and vomiting
- sweating
- poor concentration
- feeling very hot or very cold
- abdominal pain
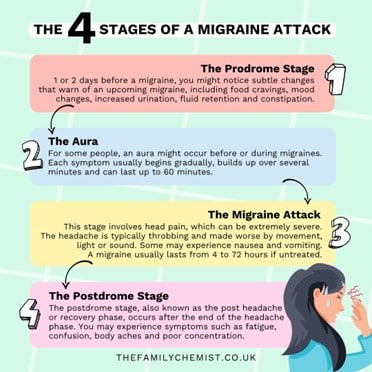
Understanding Migraine and its 4 stages
Migraines can affect children, teenagers as well as adults. It progresses through four stages:
- The Prodrome Stage
- The Aura
- The Migraine Attack
- The Postdrome Stage
Not everyone who has migraines goes through all stages. See detailed image below for more information.
What causes a Migraine Attack?
Scientists haven’t concluded an exact cause of migraines. But they still believe the condition is due to temporary changes in the chemicals, nerves and blood vessels in the brain.
There are many migraine triggers that are repeatedly reported, including:
- Hormonal changes
- Alcohol
- Stress
- Certain foods
- Changes in sleep pattern
- Tiredness
- Changes in routine
Self-Care Tips for a Migraine Attack
Treatments available
Triptans are a type of drug that is very safe to use and usually effective. They are taken at the start of your head pain and helps reduce the pain and sickness of a migraine attack. If the pain comes back, you can take a second dose within 24 hours. Like all medication, there is sometimes side effects such as tingling, flushing and drowsiness. The way side effects affect different people can vary between the different triptans. So, if one causes unpleasant side-effects, a switch to a different one may be fine. Triptans available are Sumatriptan, Imigran, Rizatriptan, Zolmitriptan and Maxalt Melt. If you are unsure, you can contact The Family Chemist for more information and advice.
Identify the signs
To conclude, whether you having a headache or a migraine attack, its important you understand the signs and what you’re going through so you can treat it accordingly. Identifying and treating headaches as early as possible can help a person’s ability to function and reduce their overall quality of life. Keeping a migraine journal can lead to faster and more effective treatment.
**Image sourced from templehealth.org



