What Happens To Your Body When You Quit Smoking?
Jump to
Quitting smoking is a significant step towards improving your health and well-being. When you stop smoking, your body begins a healing process that can lead to immediate and long-term benefits. This blog will explore what happens to your body when you stop smoking, the symptoms you might experience, and strategies for managing them.
Symptoms when you quit smoking
When you quit smoking, your body starts to repair itself almost immediately. However, this process can cause various symptoms as your body adjusts to the absence of nicotine. Common symptoms include:
- Nicotine cravings: These can be intense, especially in the first few days.
- Irritability and anxiety: Nicotine withdrawal can make you feel on edge.
- Difficulty concentrating: Many people experience “brain fog” as their bodies adjust.
- Increased appetite: Nicotine suppresses appetite, so you may feel hungrier when you quit.
- Coughing and sore throat: Your lungs begin to clear out mucus and other debris.
- Sleep disturbances: You might have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep.
Feeling emotional when you quit
Quitting smoking can be an emotional rollercoaster. Nicotine affects brain chemistry, and its absence can lead to mood swings, feelings of sadness, and even depression. It’s important to recognise these feelings as part of the withdrawal process and seek support if needed.
Weight gain and quitting smoking
Weight gain is a common concern when quitting smoking. Nicotine increases metabolism and suppresses appetite, so without it, you might eat more and burn fewer calories. Here are some tips to manage weight gain:
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Stay active: Regular exercise can help control weight and improve mood.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking water can help control hunger and keep you feeling full.

Managing smoking withdrawal symptoms
Withdrawal symptoms can be challenging, but they are temporary. Here are some strategies to manage them:
- Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT): Products like patches, gum, and lozenges can help reduce cravings.
- Prescription medications: Talk to our pharmacist about medications that can help manage withdrawal symptoms.
- Behavioural therapy: Counselling and support groups can provide strategies and encouragement.
Managing stress when you quit smoking
Stress is a significant trigger for smoking. Finding healthy ways to manage stress can help you stay smoke-free:
- Exercise: Physical activity can reduce stress and improve your mood.
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques: Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help manage stress.
- Stay connected: Lean on friends, family, and support groups for emotional support.
Costs of smoking
Smoking is not only harmful to your health but also expensive. The cost of cigarettes adds up quickly, and smoking-related illnesses can lead to high medical bills and lost productivity. Quitting smoking can save you a significant amount of money.
Benefits of quitting smoking
The benefits of quitting smoking are immense and start almost immediately:
- Improved lung function: Your lungs start to repair themselves within weeks.
- Reduced risk of heart disease and stroke: Your heart and blood vessels begin to heal.
- Better overall health: Quitting smoking reduces your risk of cancer, respiratory diseases, and other smoking-related illnesses.
- Improved sense of taste and smell: These senses can start to return within days.
- Better skin: Smoking accelerates skin aging, so quitting can improve your complexion.
If you start smoking again
It’s common to relapse when quitting smoking. If you do start smoking again, don’t be too hard on yourself. Treat it as a learning experience and try to identify what triggered the relapse. Use this information to adjust your strategy and try quitting again.
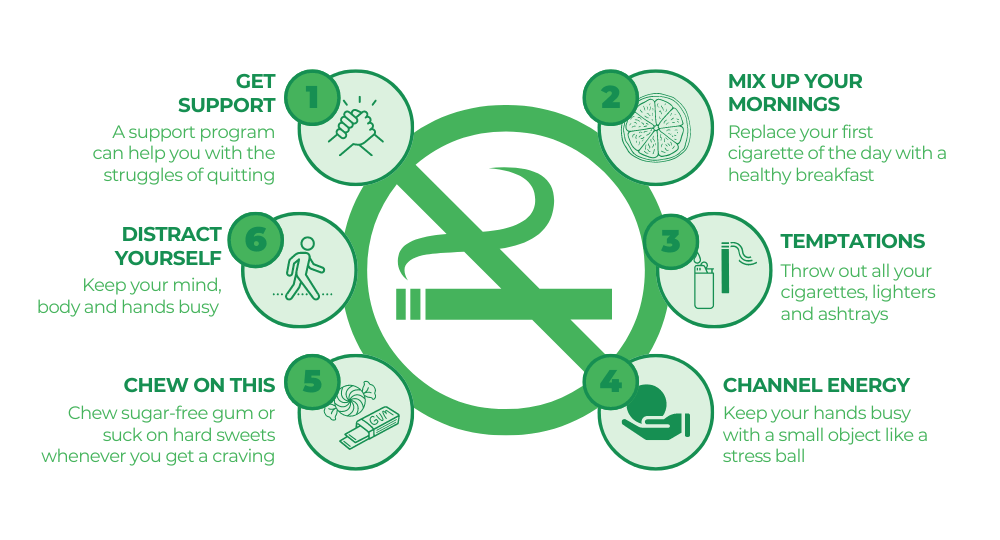
Help is available to quit
There are many resources available to help you quit smoking:
- NHS Smokefree: Offers free support and resources, including a helpline and online tools.
- Local stop smoking services: Many areas have local services that provide support and advice.
- Apps and online tools: Various apps help you track your progress and stay motivated.
Where to get help
If you’re ready to quit smoking, reach out for support:
- NHS Smokefree Helpline: Call 0300 123 1044 for free advice and support.
- Your GP: Your doctor can provide advice, support, and prescriptions for medications.
- Pharmacies: Many pharmacies offer stop smoking services and can provide NRT products.
Quitting smoking is a challenging but rewarding journey. With the right support and strategies, you can overcome withdrawal symptoms and enjoy the numerous benefits of a smoke-free life.
What is the most successful way to stop smoking
A combination of medication and counselling will both help, however, you can use a combination of the following to increase your success:
- List your reasons to quit
- Tell people you are quitting
- If you have tried to quit before, remember what worked
- Use stop-smoking medications
- Have a plan if you are tempted to smoke
- List your smoking triggers and how to avoid them
- Keep cravings at bay by keeping busy
- Exercise the urge away
What happens to your body when you quit smoking?
- Within six hours, your heart rate will slow, and your blood pressure will become more stable.
- Within one day, your bloodstream will be almost nicotine-free, the level of carbon monoxide in your blood will have dropped, and oxygen will be reaching your heart and muscles more easily.
- Within one week your sense of taste and smell may have improved.
- Within three months you will be coughing and wheezing less, your immune function and circulation to your hands and feet will be improving and your lungs will be getting better at removing mucus, tar and dust.
- Within six months, your stress level is likely to have dropped, and you are less likely to be coughing up phlegm.
- After one year your lungs will be healthier and breathing will be easier than if you’d kept smoking.
- Within two to five years your risk of heart disease will have dropped significantly and will continue to do so over time.
- Within five years, a woman’s risk of cervical cancer will be the same as if you had never smoked.
- After 10 to 15 years your risk of lung cancer will be half that of someone of a similar age who keeps smoking.
- After 20 years your risk of heart attack and stroke will be similar to that of someone who has never smoked.
What happens if you suddenly stop smoking?
Can lungs heal after 40 years of smoking?
As you progress, you will experience numerous advantages from quitting smoking, such as improved lung capacity. When you stop smoking, inactive lung cells will begin to substitute the damaged cells that line your airways. This results in gradual healing and rejuvenation of your lungs, along with a reduced risk of lung cancer.


