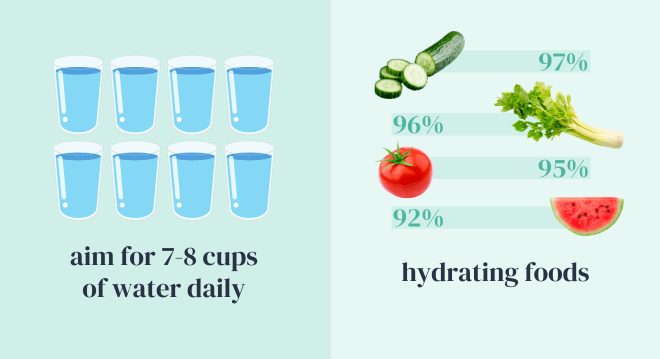5 Ways To Boost Your Metabolism
Table of Contents
Understanding metabolism
Metabolism is a term often mentioned in discussions about weight loss and energy levels, but what does it mean? Metabolism refers to the complex biochemical processes that take place within our bodies to convert food and drink into energy. This energy powers everything we do, from basic bodily functions like breathing and digestion to more demanding activities like exercise.
Key elements of metabolism
- Basal metabolic rate (BMR): This is the amount of energy your body needs at rest to maintain vital functions such as heartbeat, breathing, and cellular repair. BMR typically accounts for 60-75% of your total daily energy expenditure.
- Active metabolism: This includes the energy burned during physical activities, including exercise and daily movements. The more active you are, the higher your active metabolism.
- Thermic effect of food (TEF): This refers to the energy used to digest, absorb, and process the nutrients from food. Different foods have varying TEFs, with protein having the highest thermic effect.
Metabolism’s role in weight loss
A common misconception is that a slow metabolism is the main reason for weight gain. While metabolism does play a role in how efficiently the body burns calories, it’s important to remember that weight management ultimately depends on balancing calorie intake with calorie expenditure. By understanding the basics of metabolism, you can make informed choices about your diet and lifestyle to support a healthy metabolism and achieve your weight management goals.
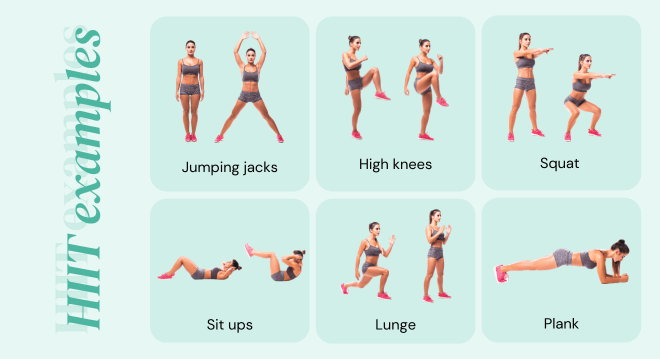
1. Incorporate high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is a powerful workout method that alternates short bursts of intense exercise with periods of rest or lower-intensity exercise. This approach not only maximizes calorie burn during your workout but can also elevate your metabolism for hours afterwards, a phenomenon known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC).
Benefits of HIIT for Boosting Metabolism:
- Increased caloric burn: Compared to traditional steady-state cardio exercises, HIIT workouts can burn a significant number of calories in a shorter period, making them an excellent option for busy people.
- Afterburn effect: The intense effort during HIIT stimulates your body’s post-exercise metabolism, meaning you continue to burn calories even after your workout.
- Muscle preservation: HIIT can help maintain and even build muscle mass, which is crucial for sustaining a higher metabolic rate, unlike some forms of cardio that may lead to muscle loss.
- Versatility: HIIT workouts can be tailored to fit any fitness level and can incorporate a variety of exercises, including running, cycling, bodyweight exercises, or strength training.
Tips for getting started with HIIT:
- Start small: If you’re new to HIIT, begin with shorter intervals, such as 20 seconds of high-intensity work followed by 40 seconds of rest, and gradually increase the intensity and duration as your fitness improves.
- Mix it up: Incorporate different exercises into your HIIT routine to keep things fresh and target various muscle groups.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to how your body responds during workouts, and allow adequate recovery time to avoid burnout or injury.
By incorporating HIIT into your fitness routine, you can significantly enhance your metabolism, making it an effective strategy for weight management and overall health improvement.
2. Protein-rich foods
Eating a diet rich in protein is one of the most effective ways to boost your metabolism. Protein plays a critical role in muscle repair, growth, and overall bodily functions. It also has a higher thermic effect compared to fats and carbohydrates, meaning your body burns more calories digesting and processing protein.
Benefits of protein for metabolism:
- Increased thermic effect: The thermic effect of food (TEF) refers to the energy required to digest, absorb, and metabolize nutrients. Protein has a TEF of 20-30%, compared to just 5-10% for carbohydrates and 0-3% for fats. This means that for every 100 calotries consumed from protein, your body may burn 20-30 calories in processing it.
- Muscle maintenance and growth: Consuming adequate protein helps maintain muscle mass, which is crucial for a higher metabolic rate. Muscle tissue burns more calories at rest compared to fat tissue, so the more muscle you have, the more calories you’ll burn throughout the day.
- Satiety and appetite control: High-protein foods can help you feel fuller for longer, reducing overall calorie intake and making it easier to manage your weight. This can prevent the common weight gain associated with a slowing metabolism.
- Improved recovery: Adequate protein intake is vital for recovery after exercise. It helps repair muscle tissue and supports your body’s adaptation to workouts, allowing you to train harder and boost your metabolism further.
Sources of protein:
- Animal sources: Lean meats (chicken, turkey, beef), fish, eggs, and dairy products (Greek yogurt, cottage cheese) are excellent sources of high-quality protein.
- Plant sources: Legumes (beans, lentils), nuts, seeds, tofu, and quinoa are great options for plant-based protein. Combining different sources can help ensure you get all essential amino acids.
Tips for increasing protein intake:
- Include protein in every meal: Aim to incorporate a source of protein in each meal and snack. This can help optimize your metabolism throughout the day.
- Experiment with protein supplements: If you’re struggling to meet your protein needs through food alone, consider protein powders or bars as convenient options.
- Plan ahead: Meal prep can help you include more protein-rich foods in your diet. Prepare meals in advance that feature protein as the main component.
By prioritizing protein-rich foods, you can effectively boost your metabolism, support muscle maintenance, and enhance overall health.
3. Stay hydrated
Remember to stay hydrated. Hydration is important for maintaining a healthy metabolism and overall bodily functions. Water is crucial for various metabolic processes, including digestion, nutrient absorption, and temperature regulation. Being adequately hydrated can help support and even enhance your metabolic rate.
Benefits of staying hydrated for metabolism:
1. Supports thermogenesis: Drinking water can temporarily boost your metabolic rate. Research has shown that consuming about 500 ml of cold water can increase your resting metabolic rate by approximately 30% for about 30-40 minutes. This is partly due to the energy required to heat the cold water to body temperature.
2. Aids digestion and nutrient absorption: Water is crucial for the digestion of food and the absorption of nutrients. It helps dissolve vitamins and minerals, making them more accessible for your body to utilize. Proper digestion ensures that your body efficiently converts food into energy.
3. Suppresses appetite: Sometimes, feelings of hunger can actually be signs of dehydration. Drinking water before meals can help you feel fuller, which may lead to reduced calorie intake. This can be particularly helpful if you’re trying to manage your weight.
4. Enhances exercise performance: Staying hydrated is essential for optimal physical performance. Proper hydration helps maintain your energy levels and endurance during workouts, allowing you to push harder and get the most out of your exercise routine. Improved performance can lead to greater calorie burn and muscle growth, both of which contribute to a higher metabolism.
Tips for staying hydrated:
- Drink water throughout the day: Aim to drink water consistently throughout the day, not just when you feel thirsty. Keeping a water bottle with you can serve as a reminder to drink more.
- Set hydration goals: Consider setting daily hydration goals based on your activity level and individual needs. A common recommendation is to aim for at least 8 cups (2 liters) of water daily, but this may vary depending on factors like age, weight, and climate.
- Incorporate hydrating foods: Many fruits and vegetables have high water content and can contribute to your daily hydration needs. Foods like cucumbers, oranges, and watermelon are excellent choices.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to signs of dehydration, such as dark yellow urine, fatigue, and dizziness. If you notice these symptoms, increase your water intake.
By making hydration a priority in your daily routine, you can effectively support your metabolism, enhance your energy levels, and improve your overall health. Remember, even small changes in your hydration habits can have a significant impact on your metabolic function.
4. Prioritise quality sleep
Quality sleep is often underestimated, yet it plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism and overall health. A lack of sleep can lead to hormonal imbalances that affect appetite and energy expenditure, making it harder to maintain a healthy weight. Here’s how prioritizing sleep can enhance your metabolic function:
The importance of sleep for metabolism:
Regulates hormones: Sleep deprivation can disrupt the balance of hormones related to hunger and appetite, such as ghrelin and leptin. Ghrelin, the hormone that signals hunger, increases when you’re sleep-deprived, while leptin, the hormone that signals fullness, decreases. This imbalance can lead to increased cravings and overeating.
Improves insulin sensitivity: Quality sleep helps maintain proper insulin sensitivity, which is essential for effective carbohydrate metabolism. Poor sleep can lead to insulin resistance, making it more challenging for your body to process sugars and increasing the risk of weight gain and type 2 diabetes.
Supports recovery and muscle growth: During sleep, your body goes through various recovery processes, including muscle repair and growth. Proper recovery is vital for maintaining muscle mass, which is crucial for a higher resting metabolic rate since muscle tissue burns more calories at rest compared to fat tissue.
Enhances energy levels: A good night’s sleep helps recharge your energy levels, making you more likely to engage in physical activities the next day. Increased physical activity contributes to higher calorie expenditure, further supporting weight management.
Tips for improving sleep quality:
Establish a sleep schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, even on weekends. Consistency helps regulate your body’s internal clock and improves the quality of your sleep.
Create a relaxing bedtime routine: Develop calming pre-sleep rituals, such as reading, gentle stretching, or practicing mindfulness techniques, to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down.
Limit screen time: Reduce exposure to screens (phones, tablets, computers) at least an hour before bedtime. The blue light emitted by screens can interfere with melatonin production, making it harder to fall asleep.
Optimise your sleep environment: Create a comfortable sleep environment by keeping your bedroom dark, cool, and quiet. Consider using blackout curtains, earplugs, or a white noise machine to block out distractions.
Be mindful of food and drink: Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime, as these can disrupt sleep. Opt for light snacks if you’re hungry, focusing on foods that promote sleep, like those rich in magnesium or tryptophan.
By prioritizing quality sleep, you can support your metabolism, enhance your energy levels, and improve your overall well-being. Making sleep a priority is a powerful step toward achieving your health and fitness goals.

5. Meal timings
The timing and frequency of your meals play a significant role in managing your metabolism and overall health. While individual preferences may vary, understanding how meal timing can affect metabolic processes can help you make informed choices for better health. Here’s how to optimize your meal timing and frequency for a metabolic boost:
1. Eat breakfast regularly
Starting your day with a nutritious breakfast can jumpstart your metabolism. Research suggests that breakfast eaters tend to have better metabolic rates and energy levels throughout the day compared to those who skip breakfast. Aim for a balanced breakfast that includes protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates to fuel your body effectively.
2. Distribute your meals evenly
Instead of cramming all your calories into a few large meals, consider spreading your food intake across multiple smaller meals throughout the day. Eating every 3-4 hours can help maintain steady energy levels, support metabolism, and prevent overeating later on. This approach may also help regulate blood sugar levels, which is essential for overall health.
3. Consider the timing of your meals
Pay attention to when you eat. Consuming a larger portion of your daily calories earlier in the day can help take advantage of your body’s natural metabolic rhythm. Research indicates that eating most of your calories in the morning and early afternoon may be beneficial for weight management and metabolic health. Conversely, late-night eating can disrupt your circadian rhythms and lead to metabolic disturbances.
4. Implement intermittent fasting
Intermittent fasting (IF) is a popular eating pattern that cycles between periods of eating and fasting. Research suggests that IF may help improve insulin sensitivity, promote fat loss, and enhance metabolic health. Common methods include the 16/8 method (16 hours of fasting and an 8-hour eating window) or the 5:2 approach (eating normally for five days and significantly reducing calories for two days).
5. Listen to your body’s hunger signals
Eating in response to your body’s hunger cues rather than strict schedules can help regulate your metabolism. Pay attention to when you feel hungry and satisfied, and try to eat mindfully. This approach can prevent overeating and help maintain a healthy weight.
6. Avoid skipping meals
Skipping meals can slow down your metabolism, as your body may enter a conservation mode to preserve energy. Make sure to plan meals and snacks, especially during busy days, to ensure you’re fueling your body adequately.
7. Stay consistent
Maintaining a consistent eating schedule can help regulate your body’s internal clock, leading to better digestion, improved energy levels, and enhanced metabolism. Aim to eat at similar times each day, which can help train your body’s hunger and satiety signals.
By being mindful of your meal timing and frequency, you can effectively support your metabolism and enhance your overall health. Implementing these strategies can help you take charge of your metabolic health, leading to improved energy levels and better weight management.
The bottom line
Understanding and optimizing your metabolism is a crucial step towards achieving your health and fitness goals. By incorporating simple yet effective strategies, such as high-intensity interval training (HIIT), fueling your body with protein-rich foods, staying hydrated, prioritizing quality sleep, and utilizing meal timing and frequency, you can empower yourself to take control of your metabolic health.
Every individual’s metabolism is unique, influenced by factors like age, genetics, and lifestyle choices. However, implementing these practices consistently can enhance your metabolic rate, promote weight management, and improve overall well-being. Remember, small changes can lead to significant results over time.
As you embark on this journey, stay mindful of your body’s signals, experiment with different strategies, and make adjustments as needed. With dedication and persistence, you can effectively boost your metabolism and enjoy the long-term benefits of a healthier lifestyle. Take charge of your metabolism today, and pave the way for a more energetic and vibrant future!